Importance of fine motor skills for school readiness
Fine motor skills make up a very large area of the activities typically completed within the school environment and these include writing, typing, colouring, cutting and drawing.
How do I know if my child has appropriate fine motor skills for going to school?
A good fine motor skill set when transitioning to primary school enables children to engage in learning activities more easily and willingly.
Transitioning to school with a good fine motor skill set is important for supporting a child’s physical coordination and endurance to participate in activities within a regular school day so that learning is fun and enjoyable, not hard and strenuous.
By the end of the year (2025), being able to complete most or all of these tasks will support your child in their transition to school in 2026. It is important to note though, that our child’s ability to do these tasks everyday can be impacted by factors such as fatigue and the business of everyday life.
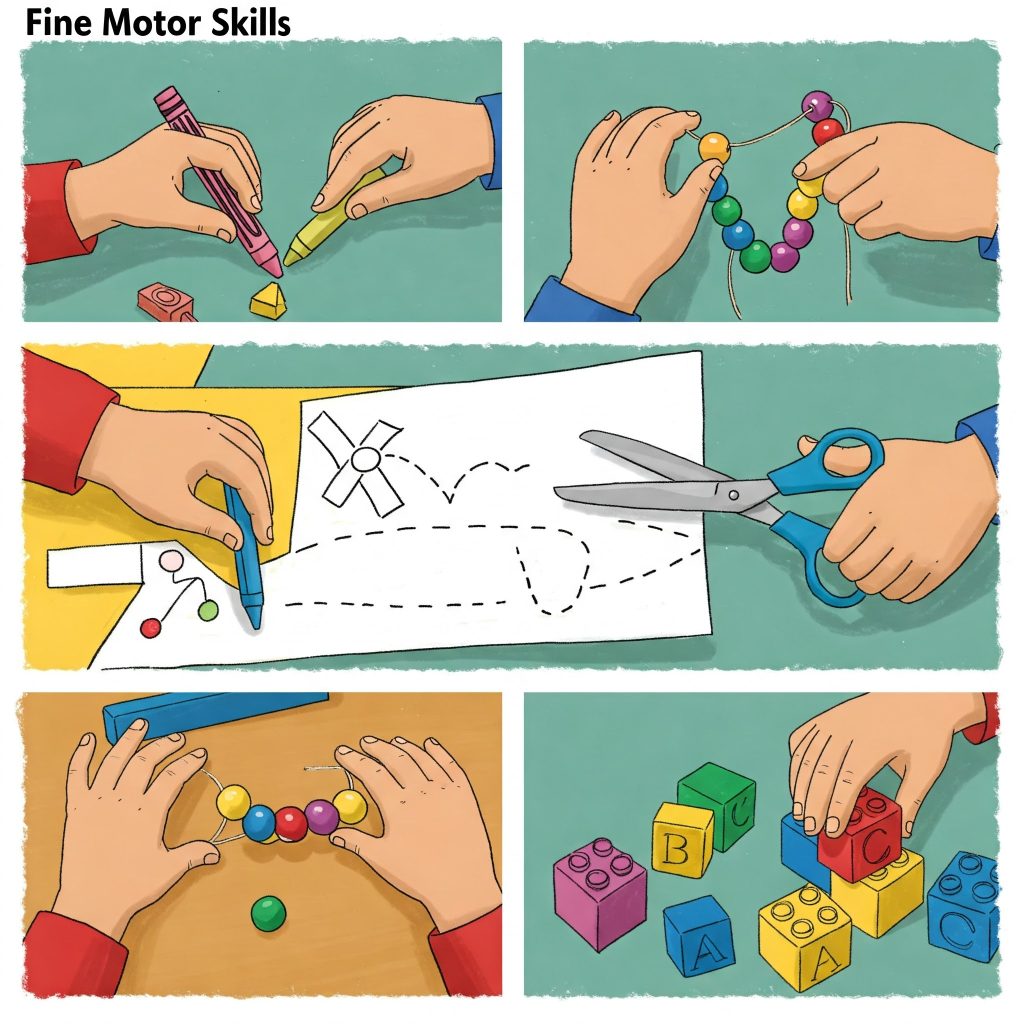
- Functional tripod pencil grip
- Using scissors to cut straight and curved lines as well as some basic shapes
- Manipulating and manoeuvring small objects using fingers (e.g. threading beads, building with small lego pieces/figurines)
- Controlled and precise movements when colouring or drawing
- Colouring within the lines
- Drawing vertical and horizontal lines, circles, crosses, squares and triangles
- Complete a simple interlocking puzzle
- Drawing simple objects, for example a person or house
- Writing own name
- Good hand-eye coordination during tasks, for example making a puzzle or building a tower from blocks
- Ability to use all fingers independently
- Established hand dominance (preferred hand for completing tasks)
Improving fine motor skills
If you are worried that your child does not appear to be school ready in this area, do not stress! There are many strategies you can use to make sure your child can go to school with an appropriate fine motor skill set:
- Practice fine motor skills through offering the child a variety of fun activities including threading, manipulation games (connect 4, pick-up sticks), play doh, construction (lego or building blocks) and crafts
- Determine hand dominance by reinforcing the child’s preferred hand frequent use for precision based activities like writing and drawing
- Practice bilateral hand-use by encouraging the child to use both when completing tasks rather than just one (e.g. building a tower out of blocks, one hand to steady and one hand to build). Card games are great for practicing bilateral integration
- Improve hand and finger strength by using pegs or clips during tasks and activities (e.g. hanging clothes or a painting to dry)
- Practice finger isolation tasks to encourage use of 1 or 2 fingers independently through activities that require poking and pinching
- Focus on enjoyment during fine motor tasks rather than successful outcomes which will increase the likelihood of the child to participate, engage and most importantly practice these skills
If this has brought up any concerns or you have any questions, please reach out to us!
Phone: (02) 6360 20 18
Email: [email protected]